ASC Compliance Documentation System
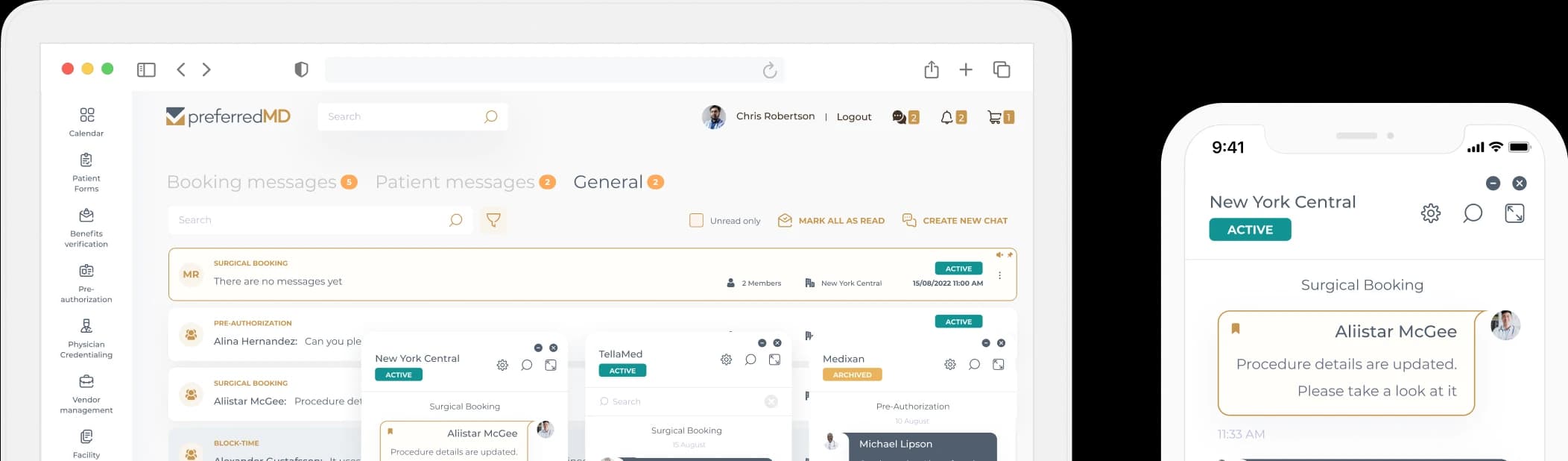
Organize policy and procedure manuals with a user-friendly platform that empowers you to effortlessly manage all documents on one page.

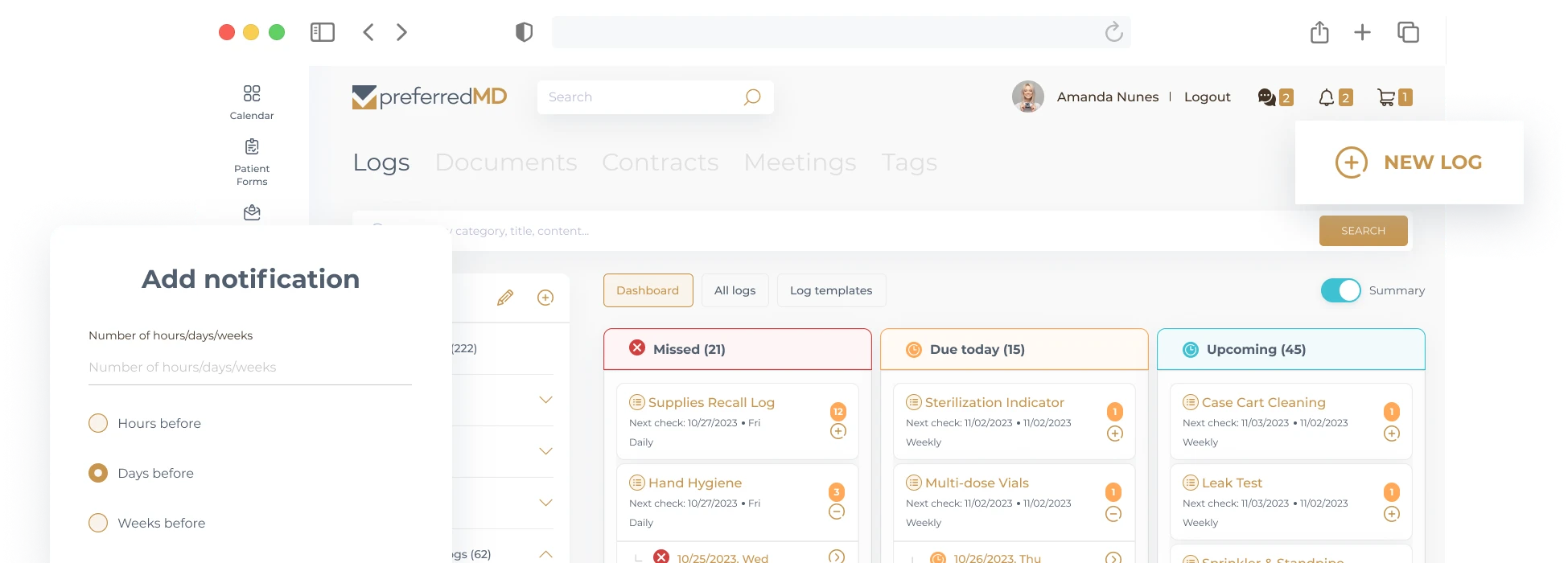
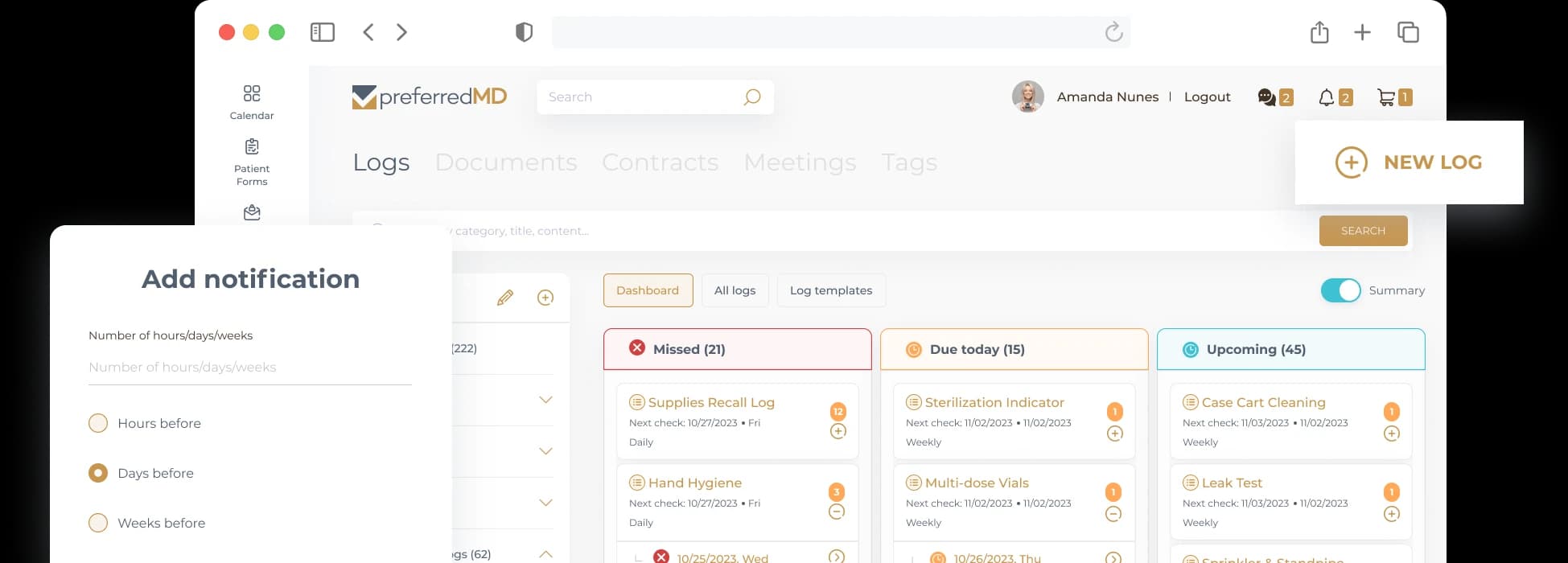
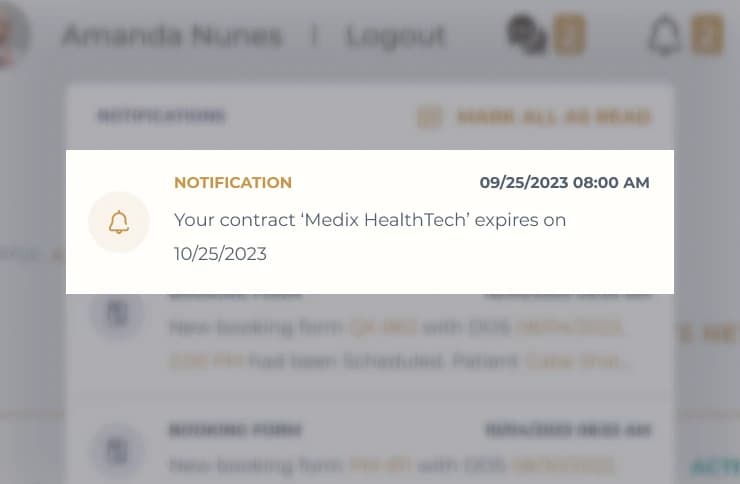
Logs




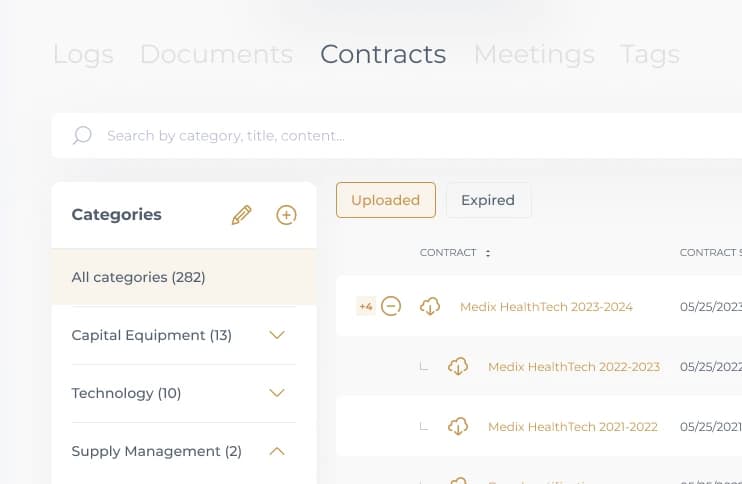
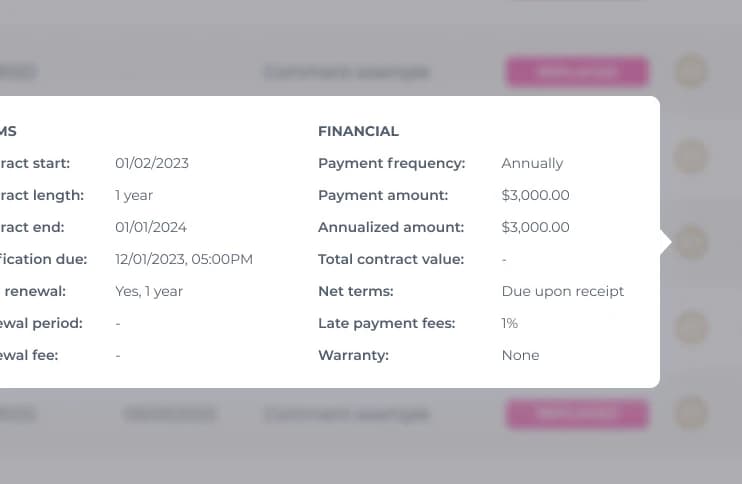
Contracts

Latest articles
Learn more about compliance and staying inspection-ready from a seasoned ASC consultant and surveyor in our blog articles.
Frequently asked questions
Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) Accreditation and Office Based Surgery (OBS) Accreditation is a formal recognition process by which healthcare facilities that provide outpatient services undergo a thorough evaluation to ensure they meet specific standards of quality and safety. This accreditation is crucial as it signifies that the facility adheres to industry-accepted practices, ultimately promoting patient safety and high-quality care.
The Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) Accreditation and Office Based Surgery (OBS) Accreditation process typically involves a comprehensive review of the healthcare facility's policies, procedures manuals, and logs. Accrediting organizations assess factors such as patient care, safety protocols, staff qualifications, facility management, and adherence to industry standards. The process may include on-site inspections, document reviews, and interviews with staff members.
Accreditation is granted by various organizations, often referred to as accrediting bodies or agencies. Examples include The Joint Commission, the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC), QUAD A Global Accreditation Authority, and the Healthcare Facilities Accreditation Program (HFAP). Different accrediting bodies may have slightly different standards and focus areas, but they all aim to ensure that outpatient facilities provide safe and high-quality care.
While Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) Accreditation and Office Based Surgery (OBS) Accreditation is typically voluntary, many healthcare facilities choose to undergo the process to demonstrate their commitment to excellence. However, some insurers, regulatory bodies, or government programs may require accreditation for reimbursement or participation. Failing to obtain or maintain accreditation may result in consequences such as loss of reimbursement, decreased patient trust, and potential regulatory actions.
Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) Accreditation and Office Based Surgery (OBS) Accreditation is usually granted for a specific duration, often ranging from one to three years, depending on the accrediting body. Renewal involves a reevaluation to ensure continued compliance with standards. Ongoing compliance is crucial because healthcare practices, technologies, and regulations evolve. Regular reviews help outpatient facilities stay current, adapt to changes, and consistently provide high-quality care, reinforcing the commitment to patient safety and satisfaction.
The Preferredmd platform can be used with all accreditation organizations including the main 3: The Joint Commission, AAAHC and QuadA.
Our platform can be used with all accreditation organizations including the main 3: The Joint Commision, AAAHC and QuadA.
Many states do require a Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) to achieve and maintain active Accreditation status in order to have procedures performed under anesthesia which may involve: moderate sedation, deep sedation, regional anesthesia, neuraxial anesthesia or general anesthesia.
A Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) can be granted Accreditation after having shown compliance with strict requirements for highest patient care, including proper equipment/safety measures/emergency readiness as well as organized and comprehensive policies and procedures for physician/staff credentialing/communication, Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) documentation, and logs. There are 3 main accreditation organizations in the United States for Ambulatory Facilities: The Joint Commission (TJC), the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC), and the American Association for Accreditation of Ambulatory Surgical Faciliies (AAAASF).
The appointed Surveyor will tour the Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) and operating/recovery rooms, including a review perioperative surgical and anesthesia quipment/supplies, safety and emergencies processes, before turning to documentation/credentialing/policies and procedures/logs to check for standard compliance. A sample of patients’ charts will be randomly selected and thoroughly analyzed. During this inspection, the Surveyor may interact with all member of the perioperative patient journey, including the Medical Director, Anesthesiologists, Credentialed Surgeons, Nurses, Physician Assistant, Surgical Technologists, and other Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) staff.
An organized Mock Survey is not required but highly recommended in order to improve readiness for the actual inspection.
Yes, once accredited, a Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) will get a certificate which should clearly be displayed for all to see.
There are required re-evaluations through a combination of self-survey and onsite surveys/inspections.
Once appropriate paperwork is completed and floor plans are approved, it takes an average of 3-6months to get accredited.
TJC was the original Outpatient Accreditation Organization, with its Ambulatory Care Accreditation Program established in the mid 1970s. Thousands of Ambulatory Facilities have been accredited through TJC; this accreditation needs to be renewed every 3 years with an average pricing of approximately $12K (spread over a 3 year period) depending on the specifics of a Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC).
https://www.jointcommission.org/
AAAHC was established in 1979. It has accredited close to ten thousands ambulatory healthcare facilities, about 50% of which are Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) and 50% are Office based Surgical Facilities (OBSs). This accreditation gets renewed every 3 years if a Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) is deemed fully compliant, and the fee varies between approximately 4K-10K (with an average of around 6K), depending on the specifics of a Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC). https://www.aaahc.org/
Accreditation assesses and evaluates a Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC)’s practices according to industry standards. Benefits of achieving accreditation includes a recognition of superior patient safety, enhanced overall reputation, as well as helping meeting some states’ requirements and some insurance provider’s requirements (Medicare/Medicaid and a growingnumber of private insurances/third party payers) for accreditation.
QuadA was first known as the American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons (ASPRS) in 1977, then changed its name to the American Association for the Accreditation of Ambulatory Plastic Surgery Facilities (AAAAPSF) in 1980, followed by a rename to the American Association for Accreditation of Ambulatory Surgery Facilities (AAAASF) in 1992. Most recently, AAAASF was renamed
QuadA in 2022. Over the the span of decades, QuadA has accredited thousands of ambulatory surgical facilities. The accreditation needs to be renewed every 3 years with an annual self-inspection to be submitted. https://www.quada.org/
Ready to reduce your operating expenses with PreferredMD?
Schedule a demo in one click
Schedule a demo